
4 mins
OpenContent Marketing In The Time of COVID-19
6 mins
In its mission to provide answers to user queries as quickly and accurately as possible, Google’s search result pages are becoming more sophisticated by the day. We breakdown all of the elements that make up a SERP.
22nd May 2020
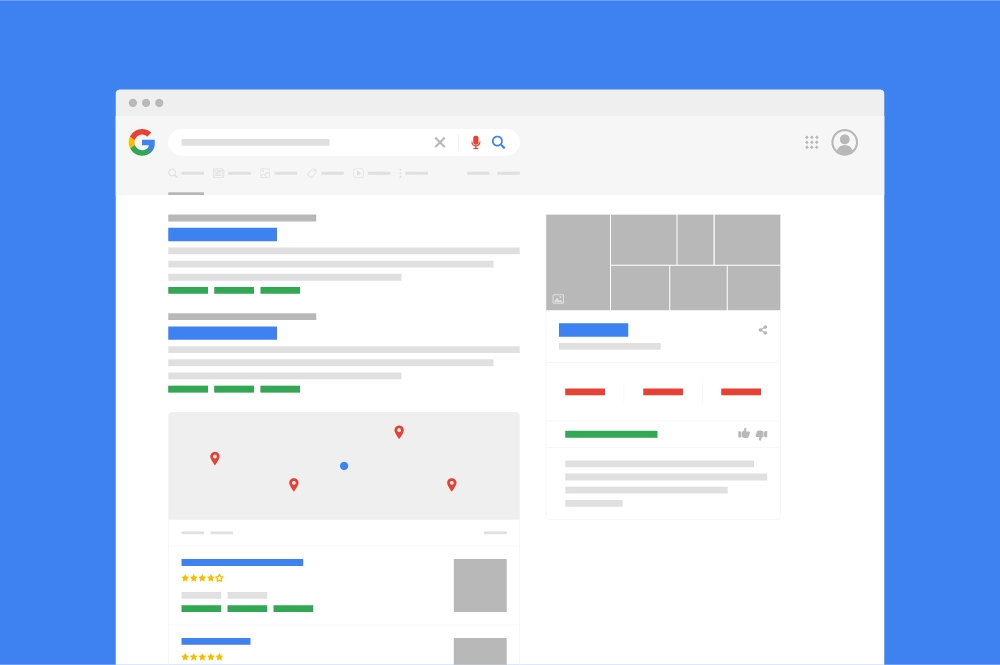
Google processes more than two trillion search queries every year, its search traffic has grown by 2000% over two decades.
When it comes to search engines, Google rules the roost in a big way. The platform processes more than two trillion search queries every year, its search traffic has grown by 2000% over two decades, and it blows competitors out of the water with over 90% search engine market share.
Google’s success is hardly surprising when you consider the effectiveness of its SERPs and the many user-friendly features that make finding an answer to a query so simple. If you’re not sure what these are or how they work, it’s time for a Go Up crash course on the wonders of Google’s SERP features!
SERP stands for search engine results page, and most of us find ourselves looking at one of these several times a day. Whenever you type a search into Google, its algorithms quickly get to work and present you with a list of web pages ranked according to relevance.
As Google aims to provide every user with a customised experience, each SERP will be unique. In addition to the query itself, the search engine also considers other factors like location and browsing history. This means that even similar searches will produce subtly different SERPs.
A Google SERP feature is anything on the page that isn’t a standard organic result. These help users gather the information they need more quickly, without them necessarily even needing to click through to a web page. Notable extra details like this provide more complete answers to search queries and a more valuable experience overall.
Google SERP features can generally be divided into two categories:
Below we’ve compiled a list of all Google SERP features so you’ll know exactly what you’re looking at when performing searches.
Stripped down HTML pages that load very quickly on mobiles. These are marked by a lightning symbol in mobile search results.
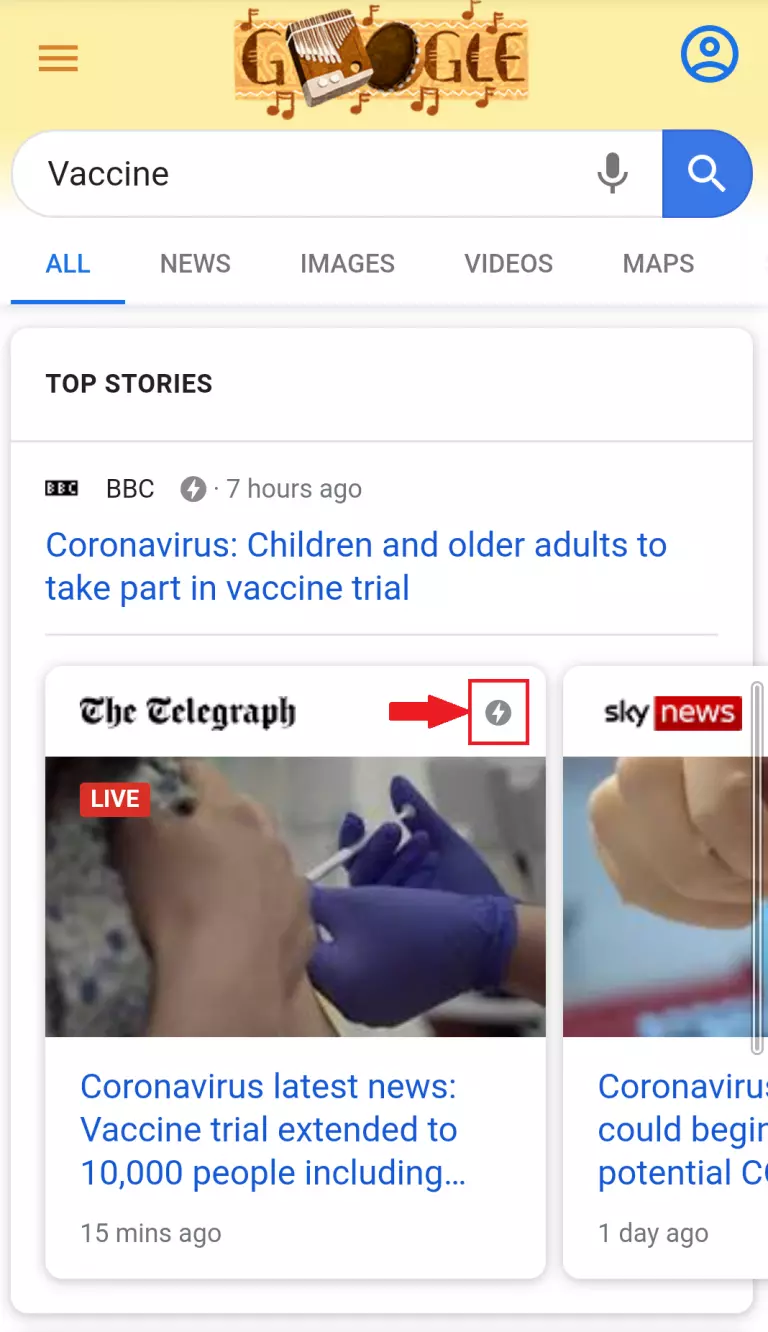 Accelerated mobile pages example
Accelerated mobile pages example
A small text path showing users where the page is on a site and how the site is structured. This appears above the metadata.
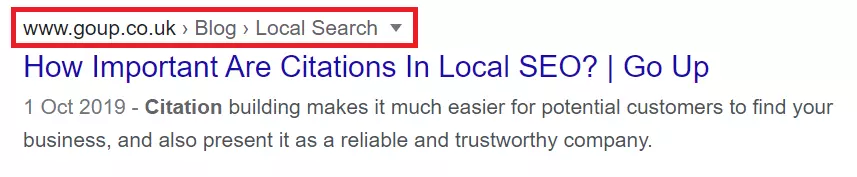
This indicates that a page has an FAQ section and previews the questions answered.
Links to podcast episodes relevant to user search queries. This content can then be played via the SERP.
The number of reviews a website has accumulated and its star rating. Review or Product Schema must be implemented on the given page in order for Google to display this in search results.
Additional links underneath a page link that point to other pages on the same website. This feature is typically displayed for branded searches, allowing one site to occupy multiple organic positions. Sometimes there may also be a search box allowing users to search the website from the SERP.
A direct and concise response to a search query. Google extracts and displays the key information from another web page so the user doesn’t necessarily need to click through to find their answer. Featured snippets come in a variety of formats including paragraphs, bulleted or numbered lists, and tables.
Other websites that Google suggests may be better at answering the query. These will often be online directories and review websites.
A horizontal row of images that link to Google Images searches.
Useful visual data instantly answering a user query. This appears at the top of the SERP and usually means a 0% click-through-rate for any sites listed below.
Google also delivers Knowledge Cards for many sports-related queries. These interactive cards feature live scores, results and fixtures, along with league tables, news and information on players and athletes.

Google aims to provide every user with a customised experience, considering factors like location and browsing history.
A carousel of cards at the top of search results in relation to a query, where clicking on a card will take you to more specified search results on that topic.
A panel on the right side of SERPs containing images and information relevant to specific brands. This data is extracted from Google My Business, Google Maps and through Organization and LocalBusiness Schema markup.
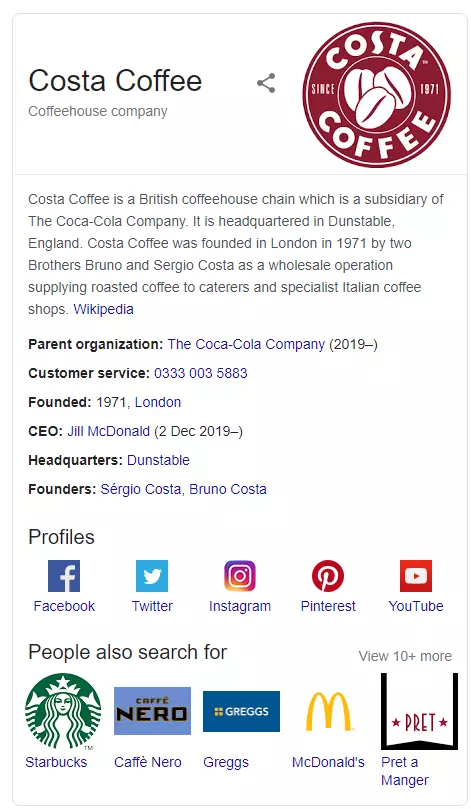
A panel on the right side of SERPs containing images and information on non-branded searches like places, objects and films. This is powered by Google’s own data as well as information extracted from other websites.
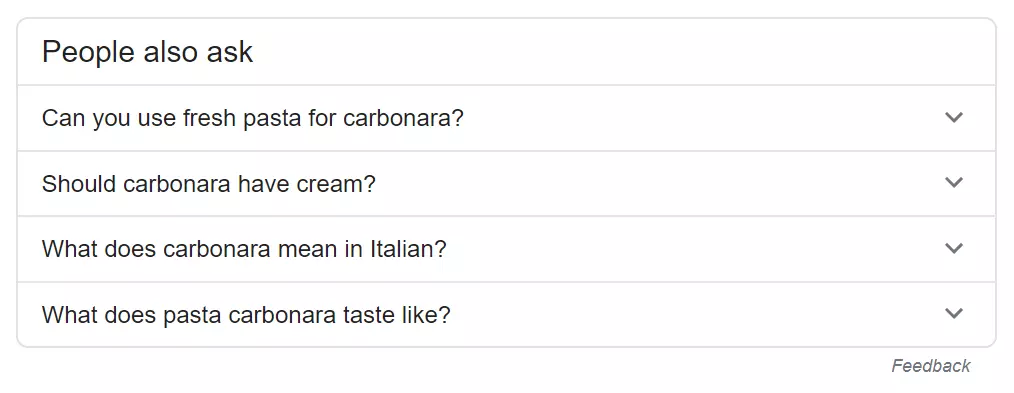
A box listing questions related to the search query. Clicking the question reveals the answer and links to the page from which Google sourced the information.
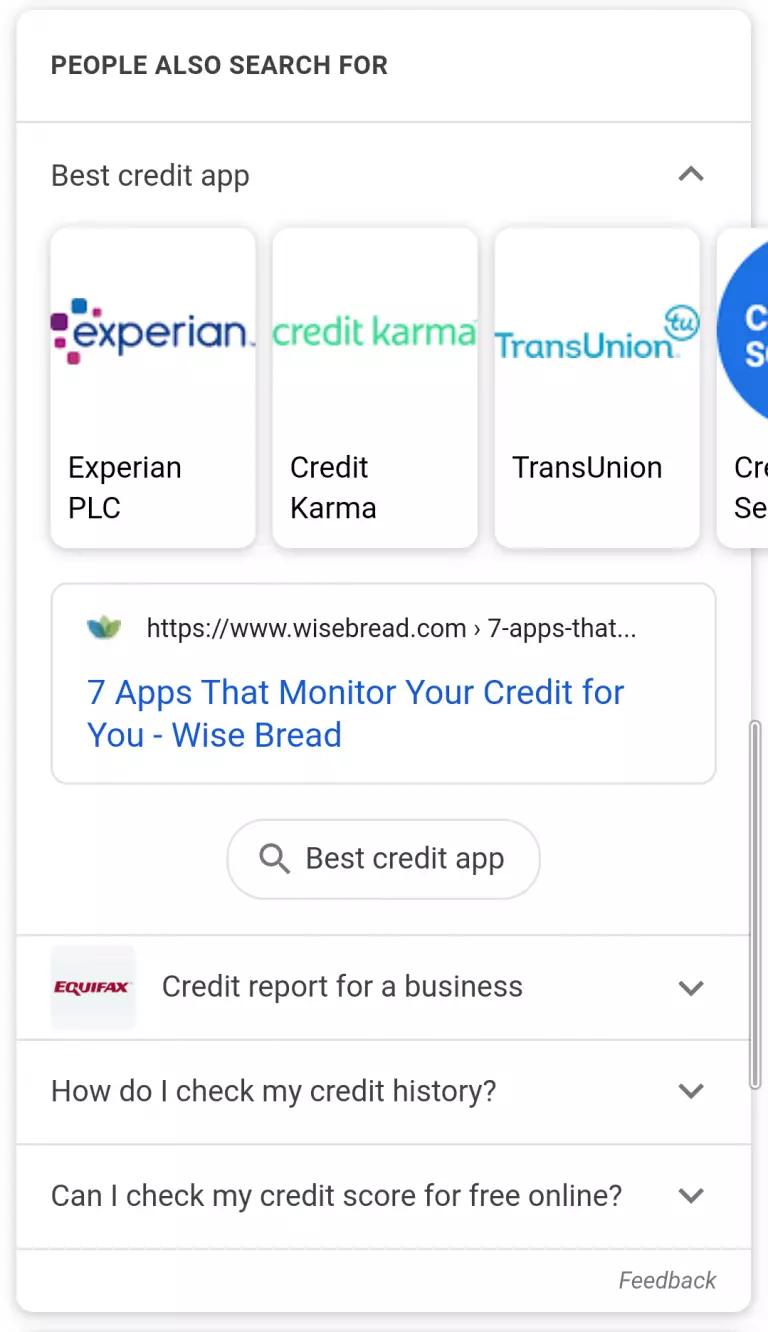
Examples of other similar search queries. These can be displayed similarly to the People Also Ask format, or if a user clicks a link then returns to the SERP, a set of related queries will appear under the original search result. Mobile only.
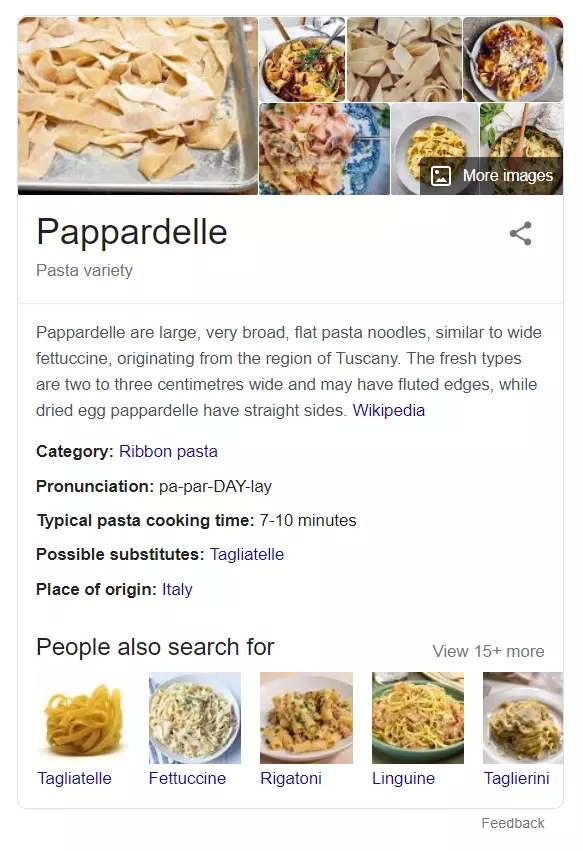
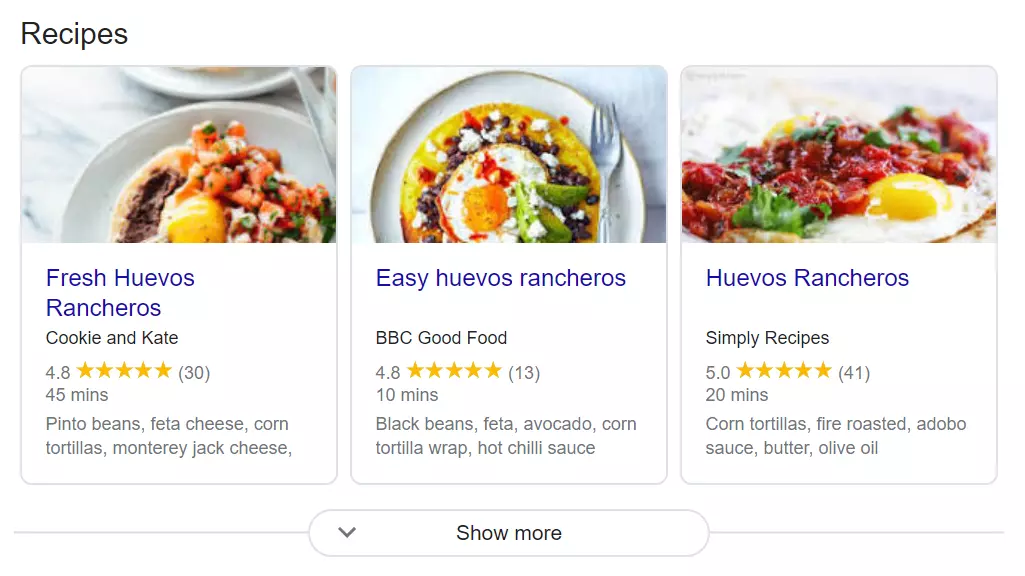
Recipes relevant to food and cooking search queries. These may all come from the same website or could be sourced from a range of different ones. More recipe cards are revealed by expanding the box vertically, whereas a carousel displays every option horizontally.
An option allowing users to make their search query even more specific. This may be by adding an additional distinctive category such as brand, style or feature.

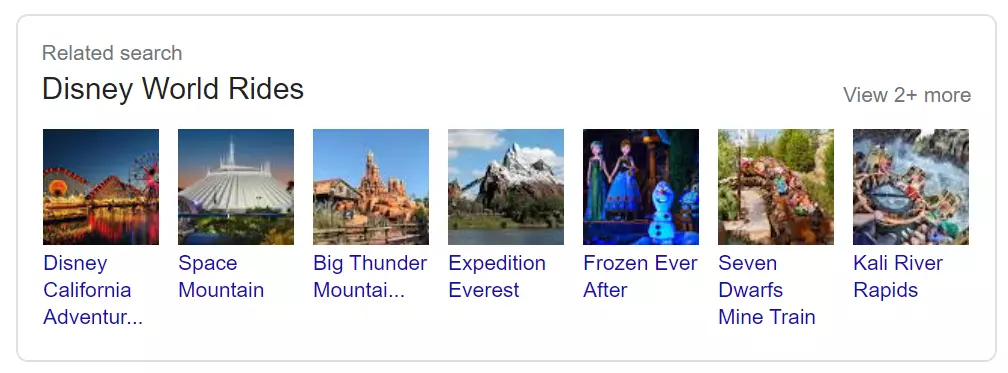
A selection of alternative search queries related to the user’s original search accompanied by image thumbnails.
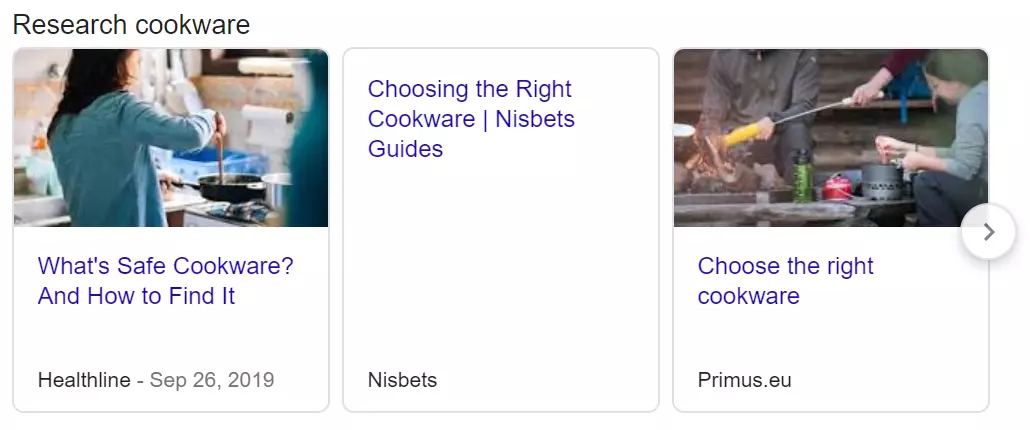
A horizontal list of links to relevant informational guides that would help users doing research around a particular search query.
A list of links to academic papers and articles that help answer a user’s search query.

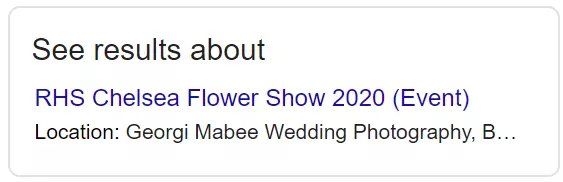
A box displaying queries very closely associated with the user’s original search. These will be displayed within a knowledge panel, including key information for each query.
Thumbnails and links to either one video or a selection of videos relevant to a user’s query.
Current news stories related to the search query in either block or carousel format.
A feature helping users easily access emergency information during a crisis. This ensures any relevant SERPs are ad-free and include links to the latest news, authoritative resources and safety tips.

A box underneath a link to a Twitter account in SERPs, previewing the most recent tweets posted to that page.
Google extracts and displays the key information from another web page so the user doesn’t necessarily need to click through to find their answer.
A carousel at the bottom of SERPs that groups similar types of location in the same area. Clicking allows users to see where these places are on Google Maps.
Informational panels that appear on the right hand side of branded search results, including information such as business address, website, opening hours, contact information and reviews. Similar to a branded Knowledge Graph panel, but as data is pulled exclusively from Google My Business, businesses have more control over what appears in this box.
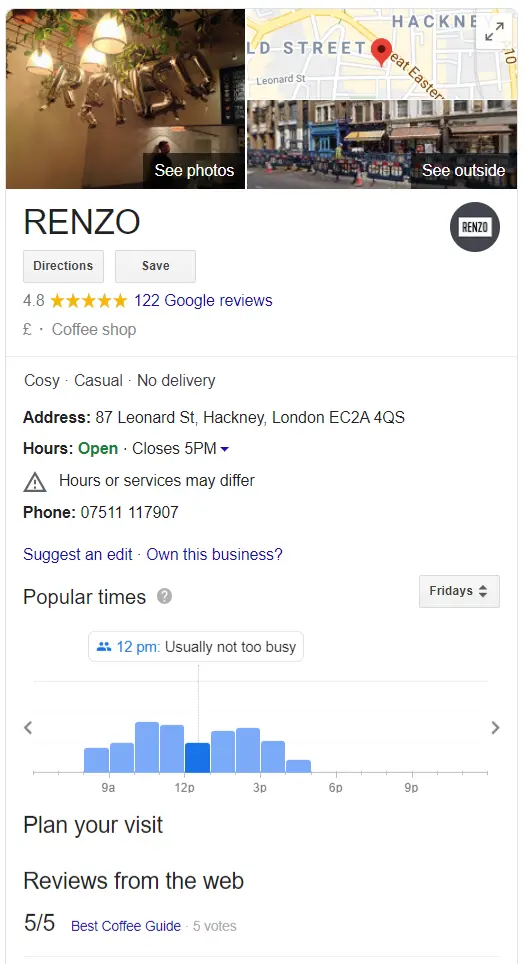
A section of SERPs highlighting three relevant, physical, nearby local businesses. This data is pulled from Google My Business (GMB), with preference given to local GMB listings with a high number of reviews and ratings. These apply to searches with local intent.
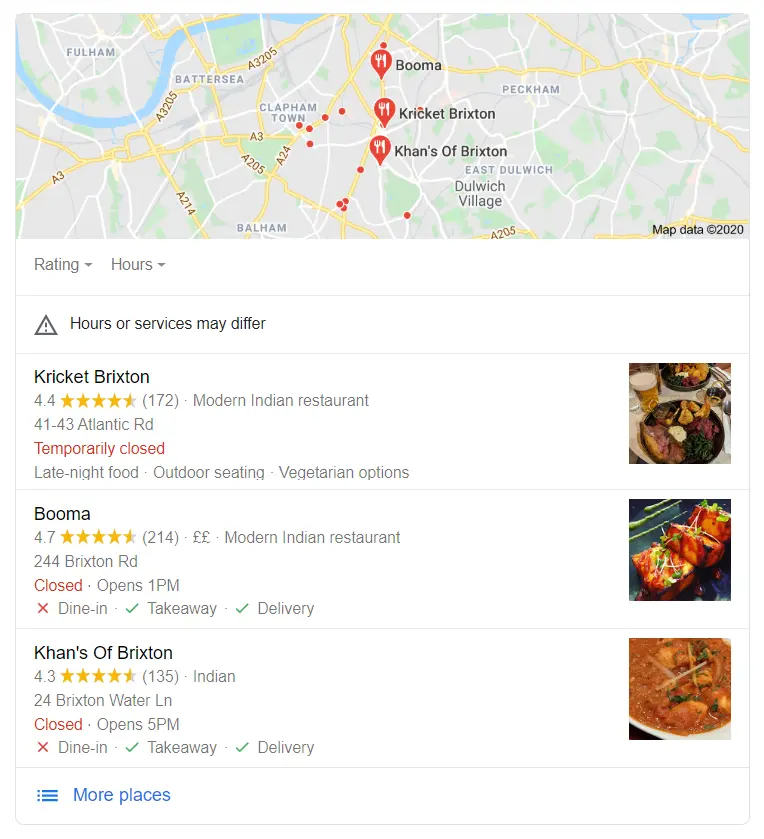
A snippet highlighting flights relevant to a search query. Users can use this to directly purchase airline tickets from third parties.
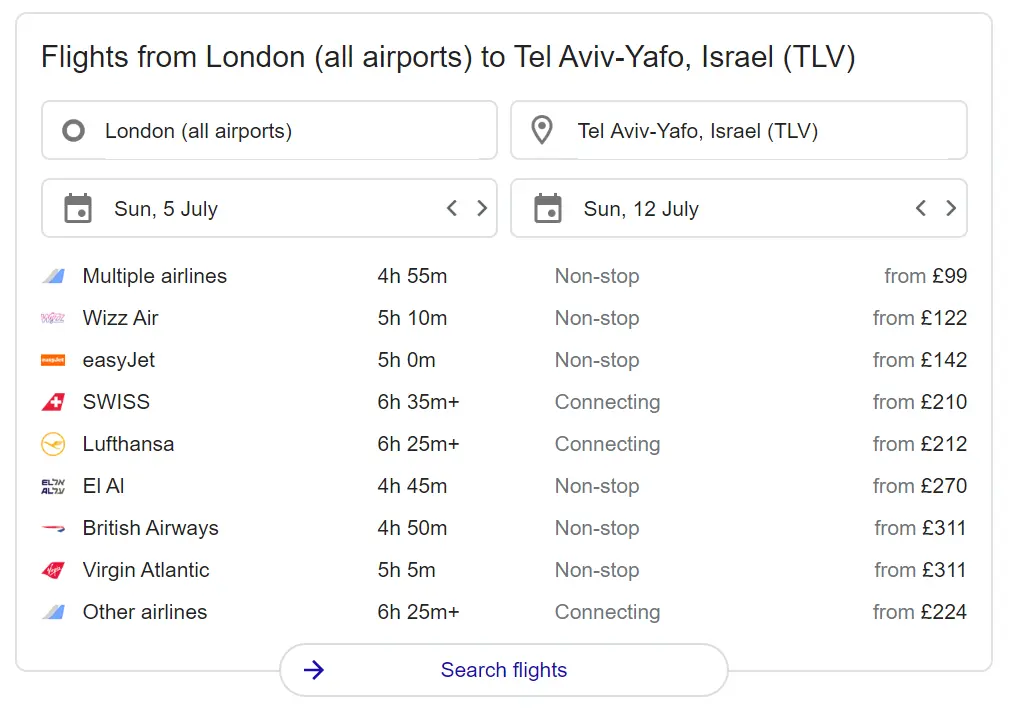
A display of hotels in the local area or the place specified in the search query. Users can use this to directly book hotel rooms from third parties.
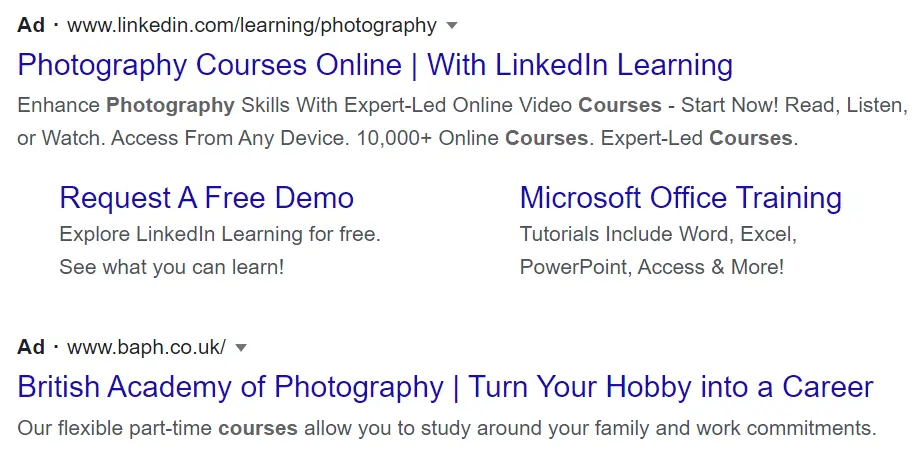
Paid-for results that typically appear above the organic search results in SERPs which are marked with the word ‘ad’. These may also be displayed below the organic listings but are less likely to attract clicks in this position. Brands pay a fee to Google each time a user clicks through to their website.
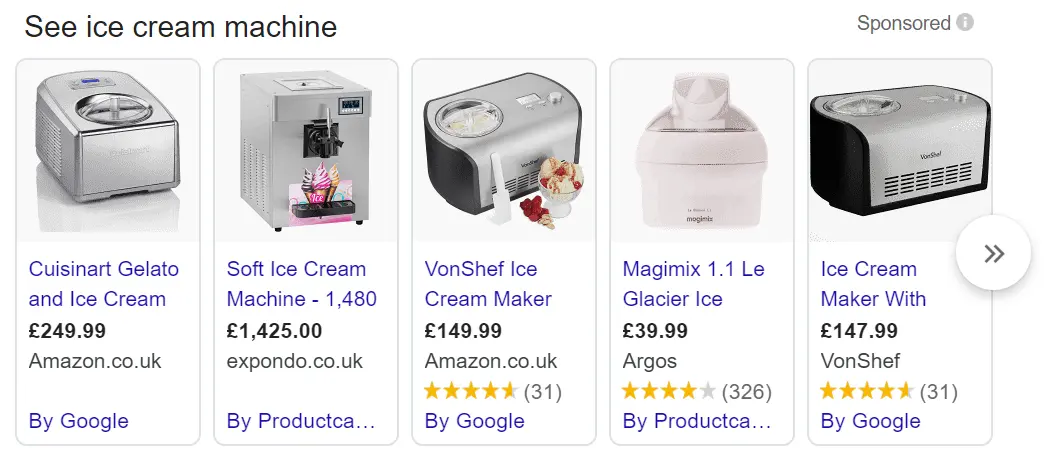
Results showing specific products matching the user’s search query. These appear either at the top or the right of the SERPs, allowing users to instantly see product images and prices.
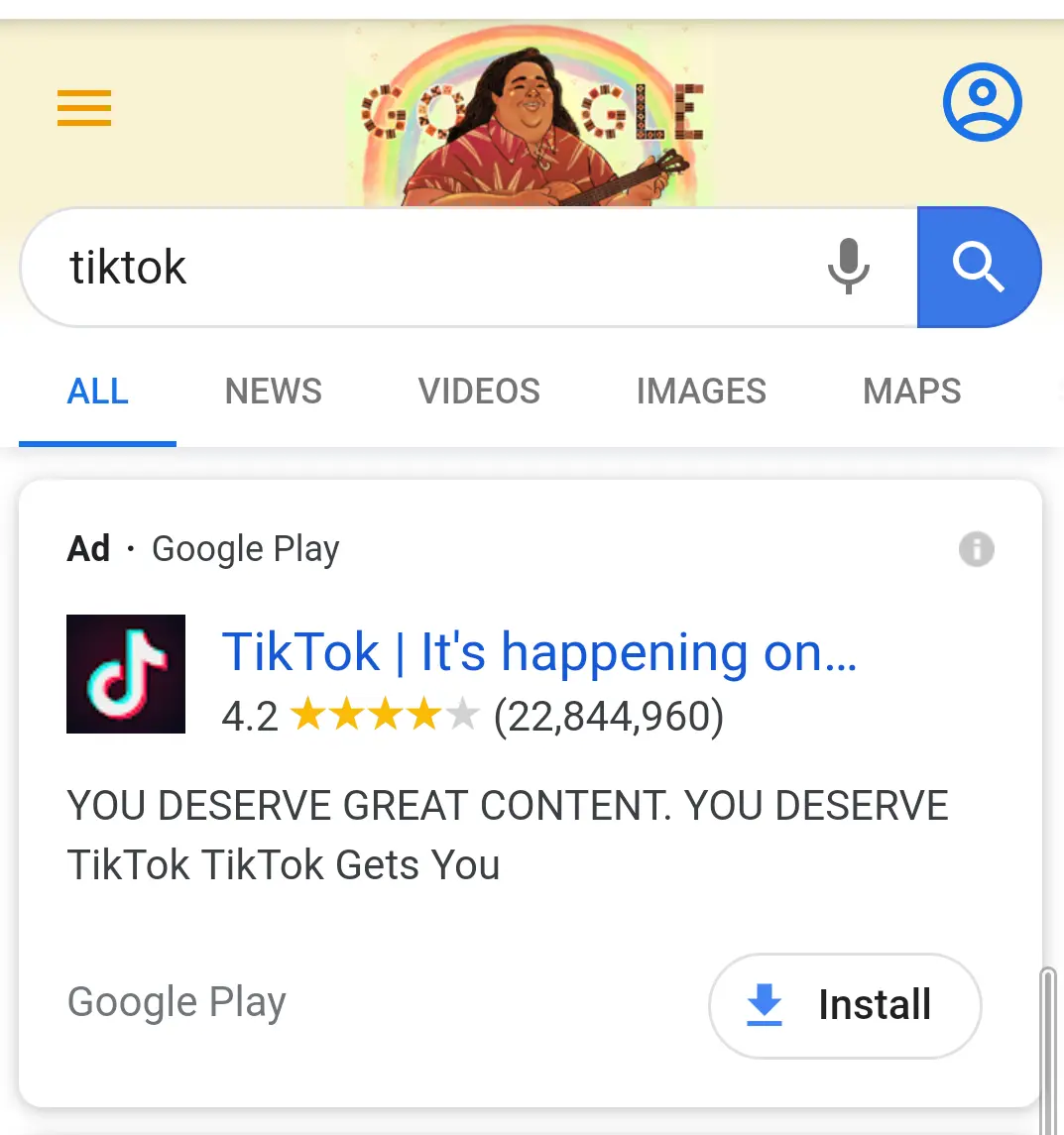
Apps relevant to the search query can be directly downloaded from mobile SERPs using Google Play.
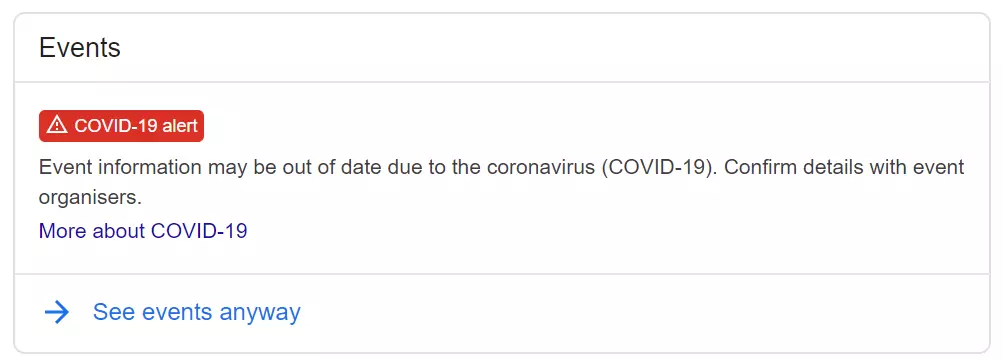
A box at the top of the SERP listing organised events in the local or specified area within the search query. Users can use this feature to obtain more information and book tickets directly.
Please note: This feature is currently suspended as a result of event cancellations due to the coronavirus pandemic. Instead, the below message is appearing where the events box would usually feature:
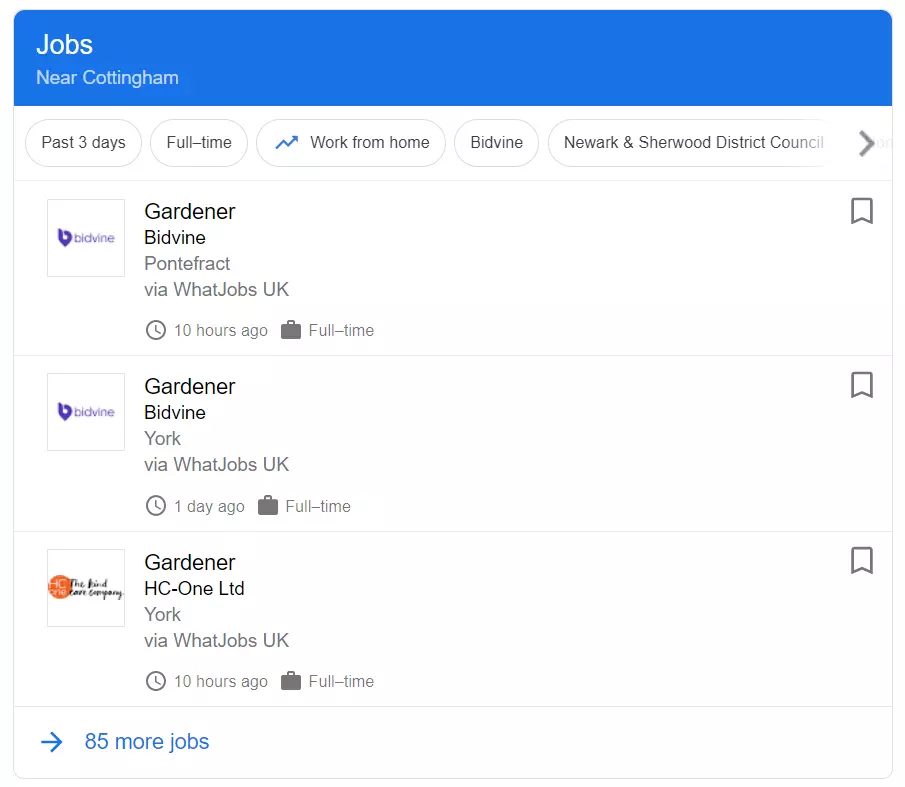
A list of job openings relevant to a user search. These adverts are taken from other websites and contain all the required information links users can follow to apply for the positions.
Google is developing existing SERP features and releasing new features all of the time, so if you spot something we haven’t covered here, get in touch with your findings and we’ll be sure to provide an explanation here.